Time:2025-11-28 Views:0 source:CNC Machining customization source:CNC Machining news
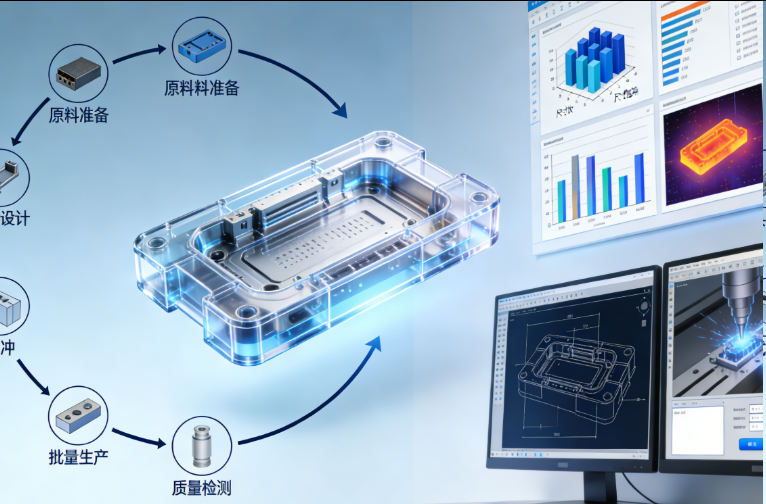
Stamping part process analysis is a comprehensive evaluation of the entire stamping workflow—from raw material preparation to finished part production—aimed at optimizing efficiency, reducing defects, and ensuring consistency. This analysis is not limited to individual steps (like bending or deep drawing) but rather examines how each process interacts, identifying bottlenecks, potential failure points, and opportunities for improvement. It is critical for high-volume production lines (e.g., automotive component manufacturing) where even small inefficiencies can lead to significant cost losses.
The analysis begins with process flow mapping, which documents every step: material uncoiling, blanking (cutting flat blanks from coils), forming (bending, deep drawing, punching), trimming (removing excess material), and finishing (deburring, coating). Each step is evaluated for cycle time—for example, measuring how long a blanking press takes to cut one blank and identifying delays like material feeding lags. Next, defect analysis is conducted: tracking defect types (e.g., burrs in blanking, wrinkling in deep drawing) and their root causes (e.g., dull punch edges, incorrect blank holder force). Statistical process control (SPC) tools are used to monitor process stability, such as tracking punch force variations over time to predict tool wear.
Material flow optimization is another key focus. Analysts check if material is being transported efficiently between stations—for example, whether a robotic arm is moving blanks from the blanking press to the forming press without unnecessary delays. They also evaluate material utilization, calculating scrap rates (e.g., how much material is wasted in blanking) and suggesting adjustments like optimizing blank layout on the coil to reduce waste. Additionally, the analysis assesses equipment compatibility: ensuring that the blanking press’s output rate matches the forming press’s capacity to avoid bottlenecks.
Finally, the analysis includes a cost assessment, comparing the cost of each process step (e.g., tooling replacement, energy usage) to industry benchmarks. Recommendations may include upgrading to faster presses, implementing automated material handling, or switching to more formable materials to reduce forming defects. By conducting a holistic stamping part process analysis, manufacturers streamline production, lower costs, and ensure consistent part quality across batches.
Read recommendations:
Sealing ring Precision electronic parts
Housing components for recessed downlights Precision electronic parts
Oval Magnetic Hardware Precision electronic parts